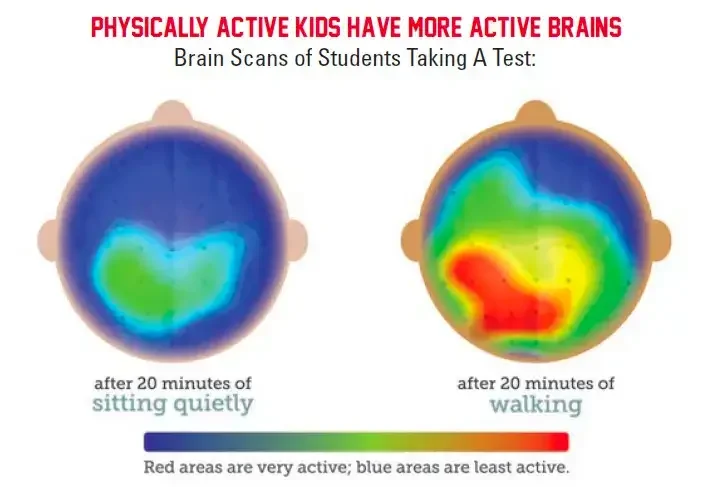
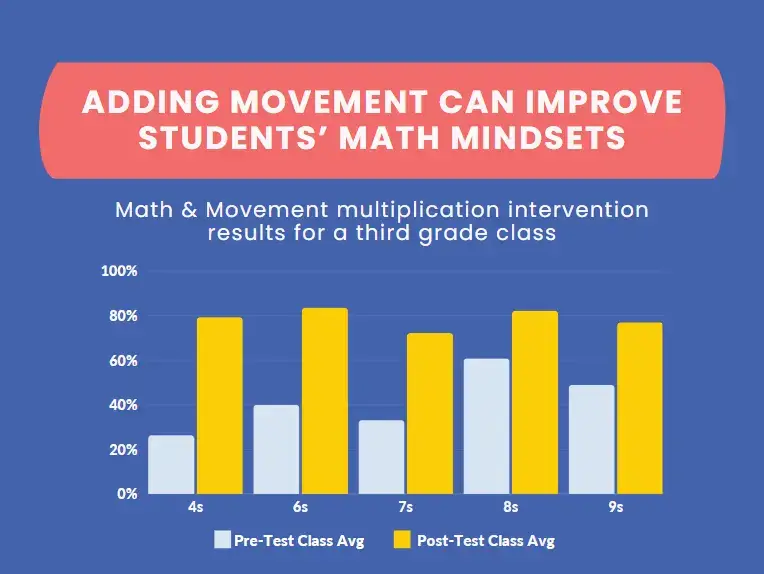
Our Product Pick
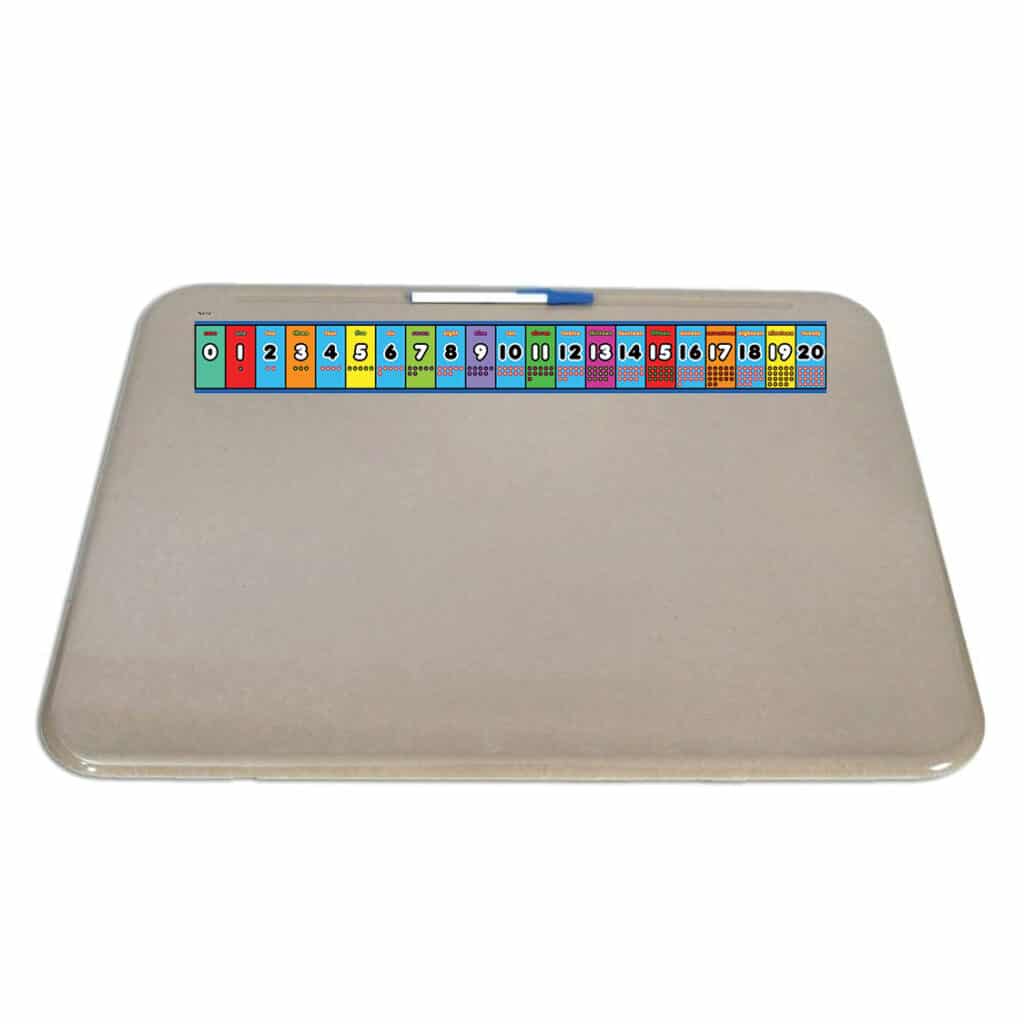

Kinesthetic activities can be done right at students’ desks with these mini number lines! Place our number line from 0 to 20 right at the top of students’ desks as a quick reference. Ideal for kindergarten and 1st grade. Available as a desktop sticker or a printable PDF.