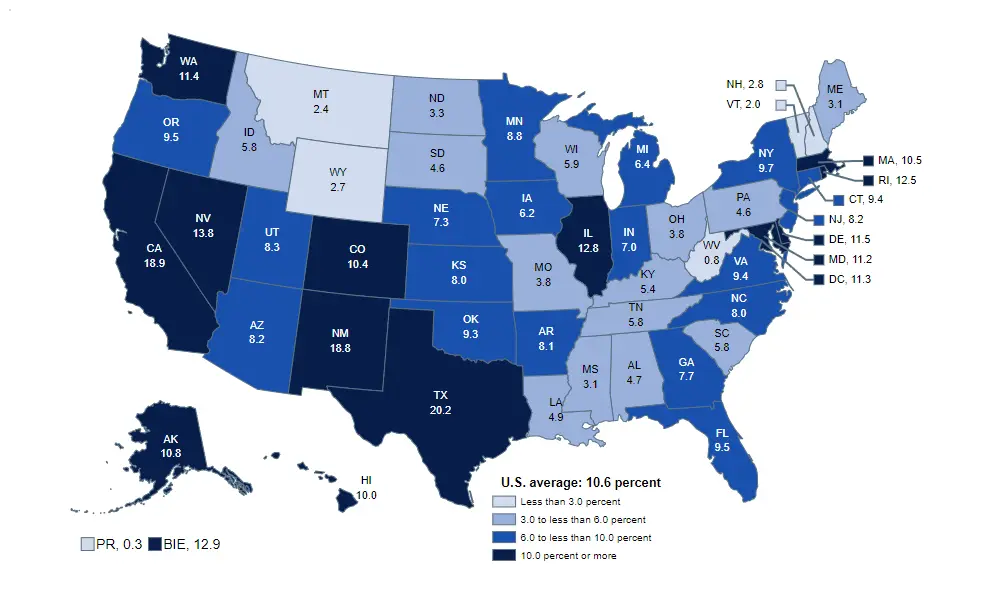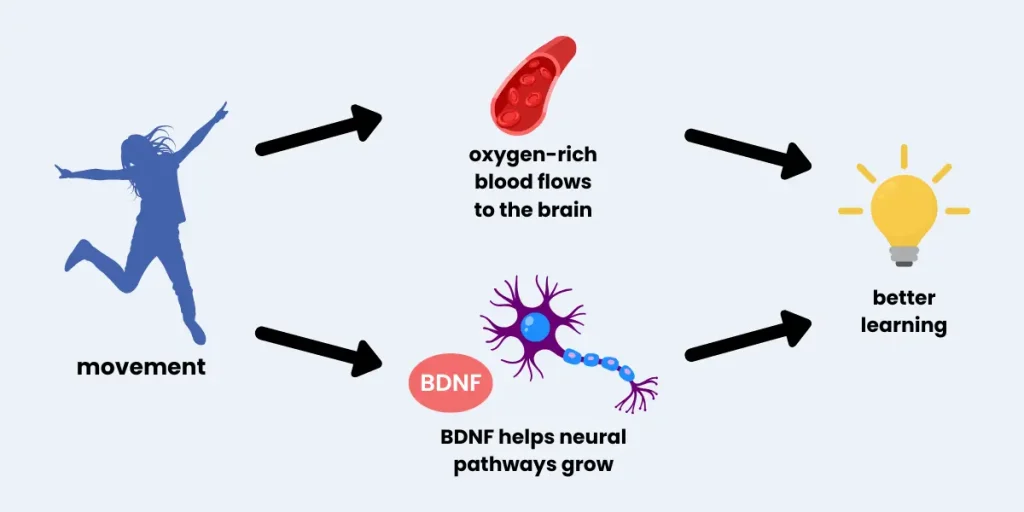
Our Product Pick

This large format number line to 20 is perfect for math lessons involving numbers 0 to 20 and skip counting by 2. Each block contains the numeral, number word, and the corresponding number of symbols for multi-dimensional learning. Multiples of 2 are in blue blocks.